Family History
Since the first report, hundreds of families have been identified with antithrombin deficiency, but it is still quite a rare condition and only affects about 1 in 5000 people. It is found in about 2 to 3% of people who have a blood clot before the age of 40yrs.
Research
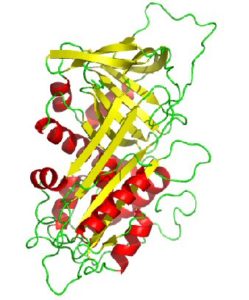 A great deal is now know about antithrombin. The DNA sequence is known and the molecular structure has been solved. In many families antithrombin deficiency is due to single point mutations in the antithrombin gene. My thesis that I did for my Doctorate in Cambridge is entitled “Antithrombin deficiency and replacement therapy”, so for several years I lived and breathed antithrombin. I played a part in identifying two antithrombin mutations known as Antithrombin Cambridge I and Antithrombin Cambridge II. I have also carried out studies on its function. Antithrombin is key to the action of heparin.
A great deal is now know about antithrombin. The DNA sequence is known and the molecular structure has been solved. In many families antithrombin deficiency is due to single point mutations in the antithrombin gene. My thesis that I did for my Doctorate in Cambridge is entitled “Antithrombin deficiency and replacement therapy”, so for several years I lived and breathed antithrombin. I played a part in identifying two antithrombin mutations known as Antithrombin Cambridge I and Antithrombin Cambridge II. I have also carried out studies on its function. Antithrombin is key to the action of heparin.
Heparin
Many of you will have received treatment with heparin at some point. It is usually administered as low molecular weight heparin as Clexane, Fragmin or Innohep. Heparin on its own is inactive and only works as an  anticoagulant when it is bound to antithrombin in the blood. Antithrombin is a very weak anticoagulant in the absence of heparin, but when they are combined in the circulation they form a complex which alters the shape of the antithrombin molecule making it a very potent anticoagulant.
anticoagulant when it is bound to antithrombin in the blood. Antithrombin is a very weak anticoagulant in the absence of heparin, but when they are combined in the circulation they form a complex which alters the shape of the antithrombin molecule making it a very potent anticoagulant.
What does it mean to have antithrombin deficiency?
If your family has antithrombin deficiency then affected members have a high risk of thrombosis, and they can occur at a very young age. If I see a child with a spontaneous DVT or PE, I immediately consider antithrombin deficiency as a likely cause. Affected people are usually put on anticoagulants for life after a single blood clot. Although clots are common with this condition, there are many people with antithrombin deficiency who never have a blood clot, so anticoagulant therapy is not recommended for affected people who have never had a clot.
Pregnancy
 The most important time to be aware of this condition is in pregnancy. Women with this condition have a very high risk of a blood clots in pregnancy and usually have low molecular weight heparin through out pregnancy even if they have never had a clot. In some studies up to 50% of women with this condition will have a clot in pregnancy if not treated.
The most important time to be aware of this condition is in pregnancy. Women with this condition have a very high risk of a blood clots in pregnancy and usually have low molecular weight heparin through out pregnancy even if they have never had a clot. In some studies up to 50% of women with this condition will have a clot in pregnancy if not treated.

Leave a Reply